Disciplina: Inglês 0 Curtidas
As to women, the text presents a tendency that has - UNIFESP 2024
The great global baby bust is under way
Across the world, birth rates are declining more rapidly than expected. That worries retired people and policymakers. In 2010, there were 98 nations and territories with fertility rates below 2.1 (known as the replacement rate) according to the United Nations. In 2021, that number had risen to 124, or more than half the countries for which data were available. The world’s 15 largest economies all have fertility rates below the replacement rate.
As the proportion of children declines, average ages rise, particularly as old people live longer (though the rise in longevity has slowed in recent years: in Britain lifespans are flatlining and in America they are falling). Some long-running demographic trends are changing, too. Educated women have for decades tended to have fewer children. Nevertheless, fertility among the less educated is now falling.
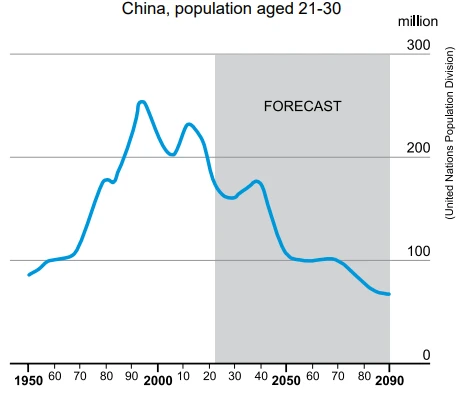
All of this poses a huge economic challenge. In parts of the world where birth rates were already low, the shortfall of young employees, who are needed to subsidise the retired, will be felt intensely. In China, the number of workers aged between 21 and 30 has already declined from 232 million in 2012, to 181 million in 2021. By the mid-2050s the United Nations forecasts there will be fewer than 100 million (see chart). China’s one-child — and later two-child — policy has contributed to the country’s decline in young workers. Recent history has shown that it is much more difficult to raise fertility levels than it is to crush them in the first place.
(www.economist.com, 14.06.2023. Adaptado.)
As to women, the text presents a tendency that has recently changed. The result of this change is:
-
two children per family to keep the replacement rate.
-
rise in longevity in developing countries.
-
educated women have fewer children.
-
variation in longevity in developed countries.
-
less educated women have fewer children.
Solução
Alternativa Correta: E) less educated women have fewer children.
A resposta correta para a pergunta é a alternativa E) "less educated women have fewer children" porque o texto destaca uma mudança significativa nas tendências demográficas relacionadas às taxas de fertilidade entre mulheres com diferentes níveis de educação. Tradicionalmente, as mulheres educadas tinham uma taxa de fertilidade mais baixa, mas o texto indica que agora as mulheres menos educadas também estão apresentando uma redução no número de filhos.
Essa mudança é importante porque sugere que o fenômeno do "baby bust" não se limita apenas a grupos educacionais mais privilegiados, mas está se espalhando por diferentes estratos sociais. O texto menciona que a queda na fertilidade entre mulheres menos educadas é uma tendência recente, indicando uma transformação nas dinâmicas familiares e nas escolhas reprodutivas. Isso pode ter implicações profundas nas estruturas sociais e econômicas, especialmente em regiões onde a mão de obra jovem é cada vez mais escassa.
As outras alternativas não refletem a ideia central do texto. Por exemplo, "two children per family" e "rise in longevity" não correspondem à mudança observada. Além disso, "educated women have fewer children" refere-se a uma tendência anterior, e "variation in longevity" não é o foco do texto. Portanto, a alternativa E é a que melhor resume a nova tendência discutida.
Institução: UNIFESP
Ano da Prova: 2024
Assuntos: Interpretação Textual em Inglês
Vídeo Sugerido: YouTube