Disciplina: Inglês 0 Curtidas
According to the chart, China’s population aged 21-30 - UNIFESP 2024
The great global baby bust is under way
Across the world, birth rates are declining more rapidly than expected. That worries retired people and policymakers. In 2010, there were 98 nations and territories with fertility rates below 2.1 (known as the replacement rate) according to the United Nations. In 2021, that number had risen to 124, or more than half the countries for which data were available. The world’s 15 largest economies all have fertility rates below the replacement rate.
As the proportion of children declines, average ages rise, particularly as old people live longer (though the rise in longevity has slowed in recent years: in Britain lifespans are flatlining and in America they are falling). Some long-running demographic trends are changing, too. Educated women have for decades tended to have fewer children. Nevertheless, fertility among the less educated is now falling.
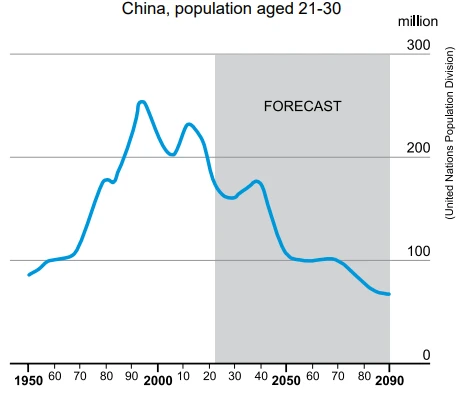
All of this poses a huge economic challenge. In parts of the world where birth rates were already low, the shortfall of young employees, who are needed to subsidise the retired, will be felt intensely. In China, the number of workers aged between 21 and 30 has already declined from 232 million in 2012, to 181 million in 2021. By the mid-2050s the United Nations forecasts there will be fewer than 100 million (see chart). China’s one-child — and later two-child — policy has contributed to the country’s decline in young workers. Recent history has shown that it is much more difficult to raise fertility levels than it is to crush them in the first place.
(www.economist.com, 14.06.2023. Adaptado.)
According to the chart, China’s population aged 21-30
-
might be the same in 2070 as it was in 1970.
-
has already reached its peak in 2010.
-
has been falling steadily since 2000.
-
should flatten after 2050.
-
has been growing from 2000 to 2023.
Solução
Alternativa Correta: A) might be the same in 2070 as it was in 1970.
A resposta correta para a pergunta é a alternativa A) "might be the same in 2070 as it was in 1970" porque, conforme indicado no texto, as previsões demográficas para a população jovem da China sugerem que a população na faixa etária de 21 a 30 anos poderá estabilizar em níveis similares aos de 1970. O texto menciona que o número de trabalhadores nessa faixa etária já caiu significativamente e que as projeções indicam uma queda contínua até 2050, o que implica que a população pode não ter um crescimento significativo até 2070.
Além disso, essa alternativa reflete uma interpretação das tendências demográficas em longo prazo. Ao sugerir que a população poderia ser a mesma em 2070 como em 1970, está se considerando que a queda acentuada já observada poderá levar a um estado de estagnação, sem um aumento relevante nas próximas décadas. Essa ideia é reforçada pela afirmação de que será difícil elevar as taxas de natalidade após uma queda tão acentuada.
As outras opções, como "has already reached its peak in 2010" ou "has been falling steadily since 2000", não capturam a possibilidade de estabilização futura, enquanto "should flatten after 2050" e "has been growing from 2000 to 2023" também não são consistentes com os dados apresentados no texto. Portanto, a alternativa A é a que melhor se alinha com as previsões demográficas mencionadas.
Institução: UNIFESP
Ano da Prova: 2024
Assuntos: Inglês
Vídeo Sugerido: YouTube